Vaping has taken the world by storm, with millions of people around the globe turning to e-cigarettes as a popular alternative to traditional smoking. But despite the widespread adoption of vaping, there are still many unanswered questions about its addictive properties. What is it about vaping that makes it so appealing to users? And why do some people find it difficult to quit? In this article, we'll explore the science behind vaping addiction and hear from a neuroscientist to uncover the truth about this rapidly growing trend. From the chemical makeup of e-cigarettes to the effects on the brain, we'll delve into the factors that contribute to vaping addiction and what it means for those who are trying to break free from this habit. Whether you're a vaping enthusiast, a concerned parent, or simply curious about the science behind addiction, this article will provide a fascinating insight into the world of vaping and the reasons why it can be so difficult to quit.
The Chemical Makeup of E-Cigarettes
To understand the addictive properties of vaping, it's important to first understand the chemical makeup of e-cigarettes. E-cigarettes typically consist of a battery-powered device that heats a liquid, called e-juice, which is then inhaled as a vapor. E-juice usually contains a mixture of propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, flavorings, and nicotine.
Nicotine is a stimulant drug that activates the reward center of the brain, which is responsible for producing feelings of pleasure and motivation. When nicotine enters the bloodstream, it triggers the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in the brain's reward and pleasure centers. This surge of dopamine is what creates the feeling of pleasure associated with smoking or vaping.
Nicotine is also highly addictive, and when used repeatedly, it can lead to physical dependence. When a person stops using nicotine, they can experience withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, and depression.
The Role of Flavorings
While nicotine is the primary addictive component of e-cigarettes, flavorings also play a role in the addictive properties of vaping. E-juice flavors range from fruity to dessert-like, and the variety of flavors available has been a significant factor in the popularity of vaping.
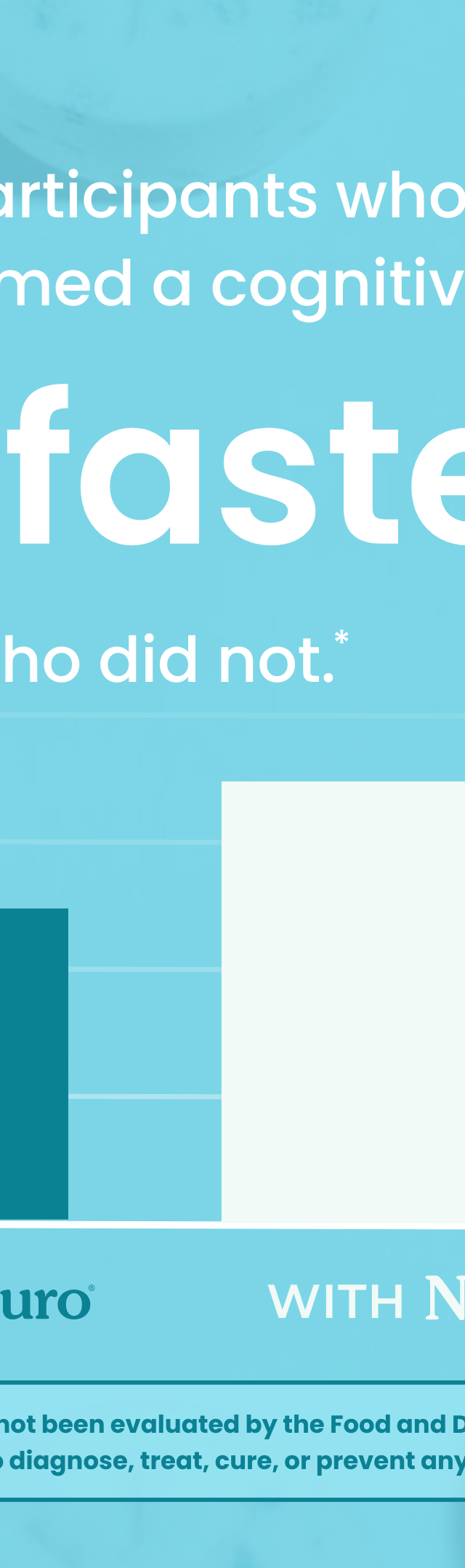
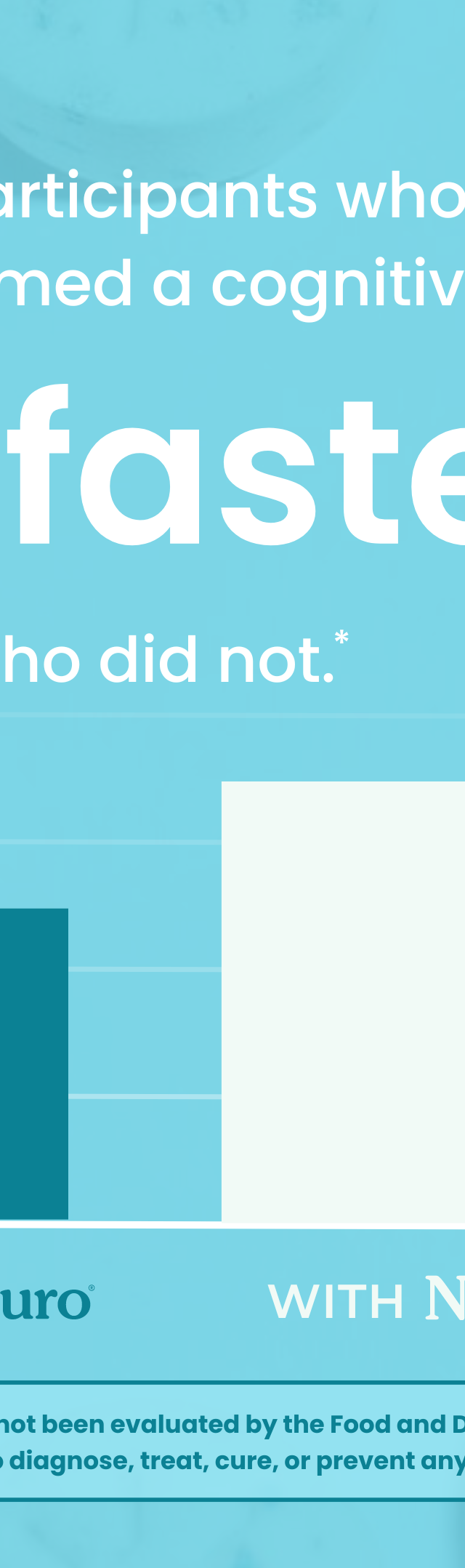
A study published in the journal Tobacco Control found that the appeal of e-cigarettes was largely due to their flavorings, with participants reporting that flavors made vaping more enjoyable and helped them quit smoking. The study also found that participants who used flavored e-cigarettes were more likely to continue using them than those who used unflavored e-cigarettes.
The addictive properties of flavorings are related to their ability to enhance the pleasurable effects of nicotine. Flavorings can also stimulate the release of dopamine, further reinforcing the pleasurable effects of vaping.
The Effects on the Brain
Vaping can have a significant impact on the brain, particularly in the areas responsible for reward and pleasure. The repeated use of nicotine and flavorings can cause changes in the brain's circuitry, leading to increased cravings and a decreased ability to feel pleasure from other activities.
Studies have found that the brains of individuals who vape show changes in the reward center, similar to those seen in individuals who use drugs like cocaine and heroin. This suggests that vaping can be just as addictive as other drugs of abuse.
Vaping can also have long-term effects on the brain's cognitive function. A study published in the journal Pediatrics found that adolescents who vaped showed decreased activity in the prefrontal cortex, a region of the brain responsible for decision-making and impulse control. This suggests that vaping can have a negative impact on brain development, particularly in adolescents who are still developing critical cognitive skills.
Why Quitting Vaping Can Be Difficult
Quitting vaping can be just as difficult as quitting smoking, due to the addictive properties of nicotine and flavorings. Individuals who try to quit vaping may experience withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, and depression.
Withdrawal symptoms can be particularly intense for individuals who have been vaping for a long time, as their brains have become accustomed to the regular release of dopamine associated with vaping. As a result, quitting vaping can feel like losing a source of pleasure and motivation, which can be difficult to replace with other activities.
Conclusion
Vaping has become a popular trend in recent years, but its addictive properties are a cause for concern. The chemical makeup of e-cigarettes, the role of flavorings, and the effects on the brain all contribute to the addictive properties of vaping. While e-cigarettes may seem like a safer alternative to traditional smoking, the addictive potential of vaping is a serious concern, particularly for adolescents and young adults who are still developing critical cognitive skills.
Quitting vaping can be challenging, but it is possible with the help of resources such as counseling, support groups, and nicotine replacement therapy. It's important to remember that the benefits of quitting vaping, such as improved respiratory health and decreased risk of addiction, far outweigh the temporary discomfort of withdrawal symptoms.
As we continue to learn more about the addictive properties of vaping, it's essential that individuals make informed decisions about their use of e-cigarettes. By understanding the science behind vaping addiction, we can take steps to prevent its negative impact on our health and well-being. For more information on the topic, read our articles The Vaping Trend: How it Impacts Adolescent Development - Insights from Neuroscience and Unveiling the Hidden Link Between Vaping and Anxiety - What Neuroscience Tells Us.
About the Author

Angelica Castillo is a communications student in the mornings, an actress in the afternoons, and a passionate diary writer by night.
She is the creative copywriter at Magnify Media Agency and is currently working on audiovisual projects. She is also interested in psychology, constantly informing herself about human conduct and looking for ways to improve mental health to help others live a fulfilling life.
Find her on Instagram here:
@aange.cas