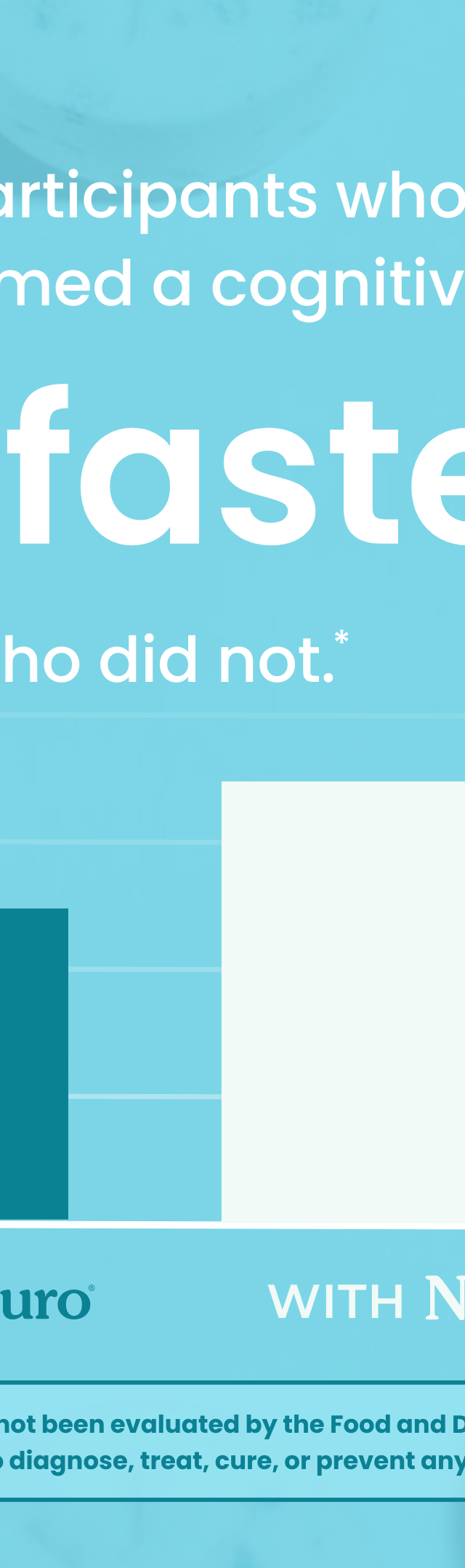
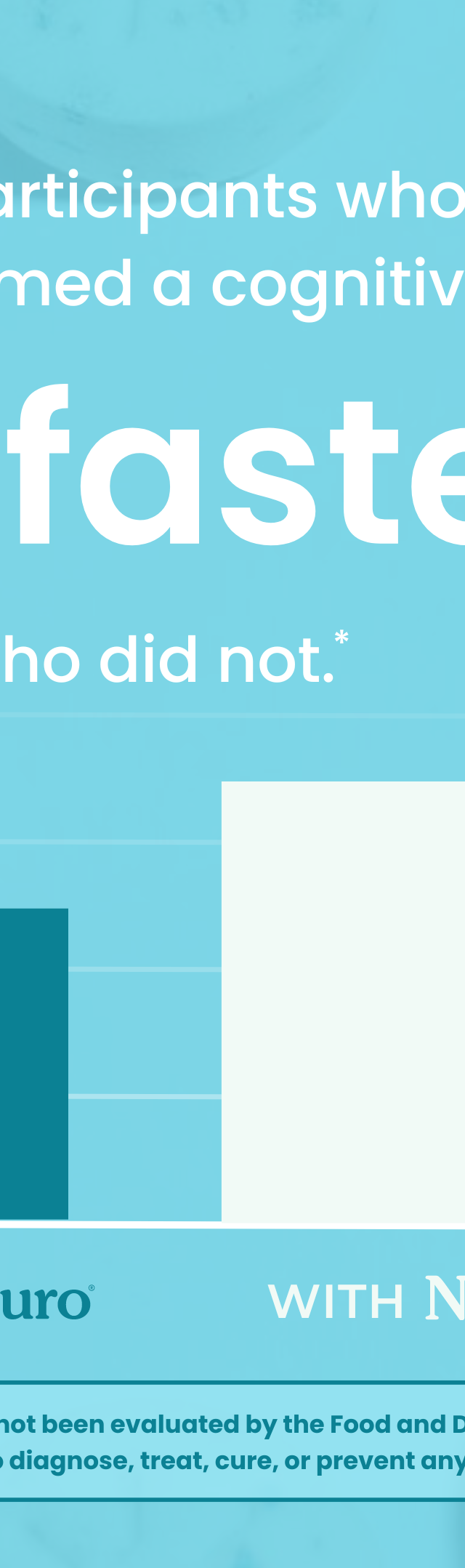
Nicotine addiction is a complex and challenging issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Whether it's the first puff or a long-standing habit, nicotine has a powerful grip on individuals, making quitting smoking a difficult journey. However, it's important to remember that nicotine addiction is not a lifelong sentence, and it isn't necessarily permanent as the brain has the capacity to undergo neuroplasticity. With the right knowledge, support, and strategies, it is possible to overcome nicotine dependency and lead a healthier, smoke-free life.
In this article, we will delve into the depths of nicotine addiction, exploring its definition, the impact it has on the brain, and the various solutions available to break free from its hold. Understanding the nature of nicotine addiction is crucial in formulating effective strategies for quitting smoking and achieving long-term success.
The exact definition of nicotine
Before diving into the complexities of nicotine addiction, it is important to understand what nicotine is. Nicotine is a naturally occurring chemical compound found in tobacco plants. When tobacco is burned and inhaled, nicotine is absorbed into the bloodstream, where it acts as a stimulant. It is this stimulating effect that makes nicotine addictive. Nicotine stimulates the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward, leading to the reinforcement of smoking behavior.
Is nicotine addiction permanent?
The notion of permanent addiction can be disheartening for those seeking to quit smoking. However, it is important to note that nicotine addiction is not necessarily permanent. While it can be challenging to overcome, many individuals have successfully quit smoking and overcome their nicotine dependency. The length and intensity of addiction may vary from person to person, but it is possible to break free from the grip of nicotine.
Numerous factors contribute to the difficulty of quitting smoking, such as the physical and psychological aspects of addiction, environmental triggers, and social influences. However, with the right approach and support, individuals can achieve long-term success in overcoming nicotine addiction.
Does nicotine rewire your brain?
One of the reasons nicotine addiction can be so challenging to overcome is its impact on the brain. Nicotine acts on the brain's reward system, causing the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. Over time, this repeated activation of the reward system can lead to changes in the brain's structure and function. These changes contribute to the development of cravings and withdrawal symptoms when nicotine is absent, making it difficult to quit smoking.
Studies have shown that nicotine can alter the connections between neurons, particularly in areas of the brain associated with reward, motivation, and decision-making. These alterations create a cycle of addiction, reinforcing the need for nicotine to maintain a sense of pleasure and well-being. However, with sustained abstinence from nicotine, the brain has the capacity to undergo neuroplasticity, allowing it to rewire and adapt to a nicotine-free state.
Solutions against nicotine addiction
Fortunately, there are various solutions available to help individuals overcome nicotine addiction. One of the most effective methods is behavioral support, which includes counseling, support groups, and cognitive-behavioral therapy. These approaches help individuals understand their addiction, develop coping strategies, and modify their behaviors to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Nicotine replacement therapies (NRTs) are another commonly used method for quitting smoking. NRTs deliver nicotine to the body without the harmful chemicals found in tobacco smoke, helping to reduce withdrawal symptoms while gradually weaning off nicotine. NRTs come in various forms, such as patches, gum, inhalers, nasal sprays, and lozenges, allowing individuals to choose the method that works best for them.
In addition to behavioral support and NRTs, medications can also be prescribed to aid in smoking cessation. These medications, such as bupropion and varenicline, work by reducing nicotine cravings and alleviating withdrawal symptoms. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable medication and dosage based on individual circumstances.
Nootropics can be used for quitting smoking
Nootropics, also known as cognitive enhancers, have gained interest as potential aids for quitting smoking. While more research is needed to fully understand their effectiveness, some studies suggest that certain nootropics may help reduce nicotine cravings and improve cognitive function during the quitting process.
One example of a nootropic that has been studied in the context of smoking cessation is modafinil. Modafinil is a wakefulness-promoting agent that has shown promise in reducing nicotine cravings and withdrawal symptoms. It is believed to work by affecting dopamine levels in the brain, which can help alleviate the reward-seeking behavior associated with nicotine addiction. However, it is important to note that modafinil, like other nootropics, should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as its effects and interactions can vary from person to person.
Another example of a nootropic that has been explored for smoking cessation is acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR). ALCAR is an amino acid derivative that has been shown to have neuroprotective effects and enhance cognitive function. Some studies suggest that ALCAR may reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms in individuals trying to quit smoking. It is thought to work by influencing neurotransmitter levels in the brain, potentially helping to restore balance and reduce the reinforcing effects of nicotine. As with any nootropic, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using ALCAR for smoking cessation to ensure it is safe and appropriate for individual circumstances.
While nootropics may hold promise as potential aids for quitting smoking, it is essential to approach their use with caution. Nootropics should always be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as they can have varying effects and interactions, and their long-term safety and efficacy are still being studied. It is also important to remember that nootropics should not be seen as a standalone solution but rather as part of a comprehensive approach that includes behavioral support, lifestyle changes, and other evidence-based strategies for smoking cessation.
Conclusion
It is crucial to recognize that quitting smoking is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Different strategies and combinations of methods may work better for some individuals compared to others. The key is to find a personalized approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of nicotine addiction.
In conclusion, nicotine addiction is a formidable challenge, but it is not a lifelong sentence. While the rewiring of the brain caused by nicotine can make quitting smoking difficult, it is important to remember that addiction is not permanent. Through a combination of behavioral support, pharmacotherapy, and lifestyle changes, individuals can overcome nicotine dependency and lead healthier, smoke-free lives.
It is essential to seek professional guidance and support when attempting to quit smoking, as healthcare professionals can provide personalized advice and recommend the most appropriate strategies and resources based on individual circumstances. With determination, perseverance, and a comprehensive approach, breaking free from nicotine addiction is an achievable goal. Remember, it is never too late to embark on the journey towards a healthier, nicotine-free future. For more information on this topic, check out our article What Makes Vaping addictive? - Truth Unveiled by a Neuroscientist and The Vaping Trend: How it Impacts Adolescent Development - Insights from Neuroscience.
About the Author

Kent Yoshimura is co-founder & CEO of Neuro, a gum and mint company that enhances your health and wellness in the most convenient, affordable, and portable way possible.
His fascination with the human brain and optimizing performance led him to get a bachelor’s degree in neuroscience at the University of California, San Diego, and after college, continued his career as a multimedia creative, filmmaker and athlete, having trained in Judo with the Japanese Olympic Judo Team and in Muay Thai at Sityodtong in Thailand.
Find him on Instagram here:
@kentaro