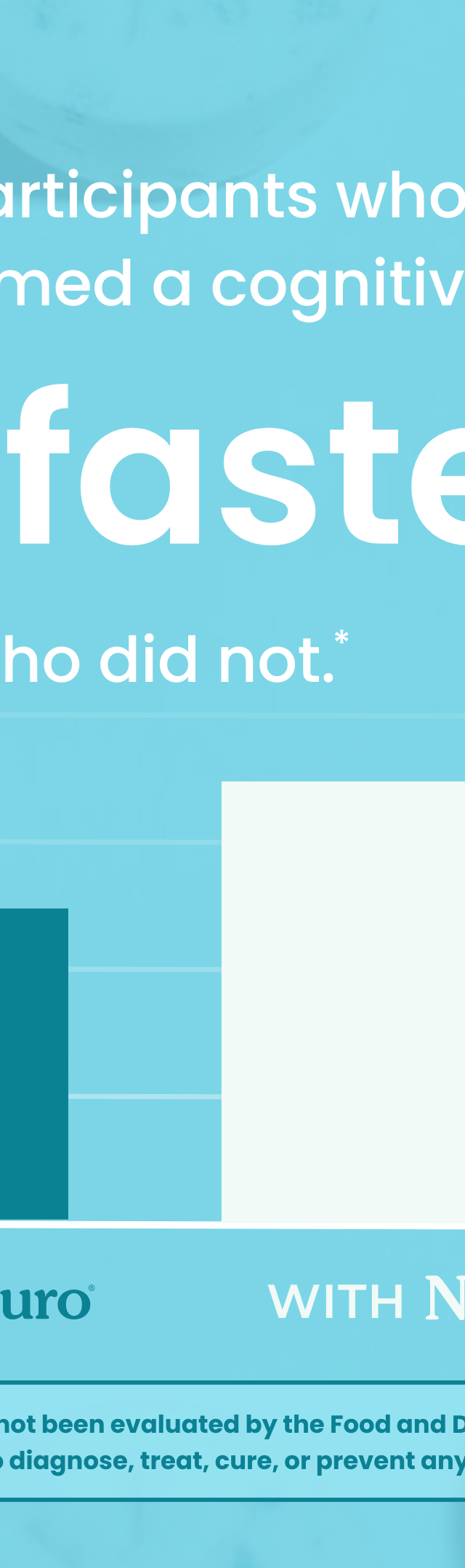
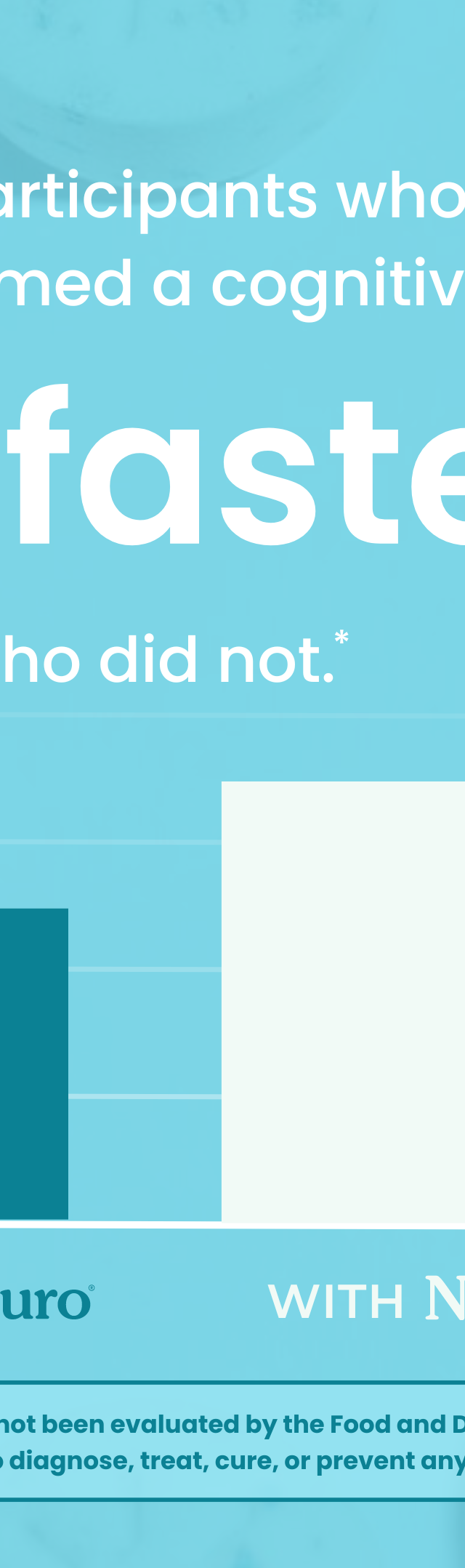
"You can't teach an old dog new tricks," is a misleading idiom that as human beings we have accepted for a long time. On the surface it appears true. Full grown adults have a strong tendency to become set in their ways.
The saying about old dogs, however, implies that it's a rule of nature that this learning becomes impossible when a person gets older.
In actuality, when we get older, we often lose neuroplasticity, which causes this perception.
What is Neuroplasticity?
Neuroplasticity or Brain Plasticity are just terms for the capacity of the brain to change and grow with time. It's a measurement that can be increased or decreased via a variety of factors.
That's why the topic is interesting. As science progresses, it becomes more clear that we can consciously increase our neuroplasticity, our capacity to learn.
Now, when your mom tells you that she can't learn to use her new computer, you can tell her she's just not trying hard enough and feel confident in your accusation! Seriously though, as a person with aging people in my life, I hear all the time from people that they're too old to figure out something new.
But while I have family in their fifties who claim to be unable to learn the iPhone, I've got a grandmother in her nineties who is an active user of her iPad, laptop, and has learned to keep in touch with the world through Facebook.
The difference here is either learned helplessness neuroplasticity, or a combination of both.
How does Neuroplasticity work?
You've likely been taught that the different regions of the brain are responsible for different aspects of your mental capacity. Like "you make decisions in the frontal lobe".
The things you've learned in this regard are generally the way a brain arranges itself after it is done forming its major connections throughout life.
Sometimes though, a region of the brain is damaged in irreparable fashion. A person might lose access to part of their brain, and this is when things get interesting.
Something called cortical remapping can occur when a part of the brain is lost, and when this happens, an entirely different region of the brain takes over the function of the lost section.
You've likely heard stories about miraculous recoveries. People "learning to talk again". This is basically how it happens.
In youth, we see this far more readily. A young mind is very plastic. It changes. So if you lose a part of your brain as a child, the rest of your brain matter as a good chance to reconnect those pieces and reallocate the remaining brain tissue.
Children are more naturally capable of these changes, which is why we say they learn languages much more easily, but as adults we can also access this ability to write new connections into our brains.
You see, neuroplasticity may be a feature that we have as a response to the risk of brain injury, however forging new connections in the brain is something that can be done with a fully healthy mind. It just needs a bit of coaxing to become more plastic again the older we are.
In recent years since the community has rallied around the idea that we can build fresh neurons as well as change these pathways, the productivity and lifehacking crowd has been diving deep into trying to find ways to increase this ability, to help adults learn new skills with the ease that children do.
While there isn't a pill you can take just yet, there are plenty of things you can do to increase your brain's ability to forge new pathways, unlearning negative habits and acquiring new ones.

You're going to get tired of me telling you to exercise. It basically helps all forms of self-improvement, however, so you need to get used to it.
Exercise increases blood flow to the brain and the production of hormones that encourage neuron growth and the connection of new neural pathways.
Reading

Watching television is not always bad, but the fact that it has nearly entirely replaced reading in our recreational time is a massive loss for our brains. Reading allows you to step into the thought process of another human being who thinks in novel ways.
Think of it as using someone else's neural pathways to teach your own mind how to build those same roads. As you read their thoughts, in the way they connect them, you too will come to associate the same topics, creating new connections and associations.

Just last night I spoke with someone who told me they have been using mindfulness meditation to unlearn the negative ways they had come to view the world.
Mindfulness meditation lets us more actively keep track of our thoughts, and in so doing, allows us to 'see' where our thoughts go from one moment to the next, and consciously control them.
Establishing this kind of discipline and control over our thoughts is not just something we perceive, but something that becomes reality.
Check out our article on getting started with meditation for tips.
Go Learn New Tricks
If you are looking for more information on Neuroplasticity, there is a lot available, but I would start at the Wikipedia entry, and when you wrap up check out this in depth guide to how it works and how to enhance it.
Here's some other articles you may also be interested in:
5 Habits for Boosting Your Brain Power
Benefits of Meditation You Might Not Know
Get Your Excercise Mojo Back
Hi! We’re Team NeuroGum, aficionados of all things brain-related, from creativity to working out. With backgrounds in art, science, and athletics, we love delving into all the potentials of the human body.
We also created the world’s first cold-compressed nootropic caffeine energy gum, made help you optimize your mind — anywhere, anytime. Find out more here.